By Dr. Burak ÇIVITCIOĞLU Associate Professor at aivancity in Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning & Deep Learning
Since the start of the AI revolution — let’s call that the release of ChatGPT-3 — the capabilities of large language models (LLMs) have been accelerating rapidly.
Let’s put this into perspective :
Just a few months ago, Veo 3 didn’t exist — and now, it’s setting new benchmarks in video generation.
A little further back, we were just beginning to see improved reasoning with Claude Sonnet 3.5 and GPT-4o.
Today, GPT-4o is the baseline. We use it for quick responses, not necessarily deep reasoning.
Since December 2024, we’ve entered what is now called the era of reasoning models. It began with o1, which has already been replaced. Now, we have access to o3, OpenAI’s most advanced reasoning model — as of today.
And yet, somehow, it already feels like these tools have always been with us. It’s hard to believe ChatGPT launched just 2.5 years ago.
What About the Cost of Intelligence ?
It’s not enough to talk about smarter models without talking about how cheaper they’ve become. Let’s get specific.
LLM pricing is typically measured in price per one million tokens.
A token is basically a chunk of a word.

- “Learning,” for example, contains about 2 tokens.
- A standard A4 page has around 600 tokens.
- A typical novel? Roughly 100,000 tokens.
- So, 10 novels is around 1 million tokens.
Now let us pause for a second. Can you guess what 1 million tokens might cost today, and what they cost when ChatGPT was first released?
Here’s the reality :
- In 2020, GPT-3’s beta launch came in at $50 per million tokens.
- Today, GPT-o3 — the most advanced model available — is just $2 per million tokens.
- And GPT-4.1-nano, a faster and cheaper model, comes in at just $0.10 per million tokens — that’s 500x cheaper than the original GPT-3.
Worth noting: the cheapest model today is still more capable than GPT-3 in 2020.
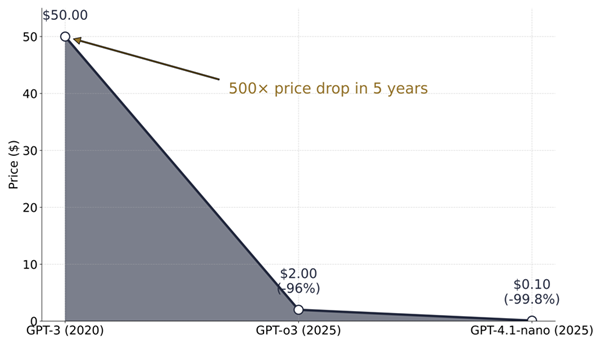
This massive price drop changed everything. It unlocked access for researchers, developers, and hobbyists. Some models, like Mistral, are free for educational or personal use under the right conditions.
But how does this relate to AI Agents ?
What is an AI Agent ?
OpenAI defines it simply:
“Agents are systems that independently accomplish tasks on your behalf”
Here’s how that works in practice :
- Task: The agent receives a natural language task.
- Plan: It breaks that task down into subtasks using LLMs.
- Tools: It executes the plan using tools — like browsing the web, running a script, or querying a database.
Let’s say you ask an agent to “find information about Aivancity School of AI and Data for Business and Society, its ranking and educational quality.”
Here’s what happens:
- The agent interprets the request.
- It builds a plan, maybe starting with search queries, followed by summarizing articles, then fact-checking.
- It uses tools like a browser to execute.
As a result, the agent will find that aivancity is 1st in France according to Eduniversal rankings of schools of AI and Data Science.
So you can think of an AI agent as having three main pillars:
- A task to complete
- A plan to follow
- A set of tools to use
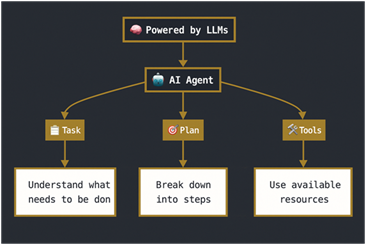
Behind the scenes, all of this is made possible by LLMs: understanding what you say, deciding what to do, and executing with awareness of tool limitations and capabilities.
Why Is This a Big Deal ?
AI Agents have existed as a concept for a while. What’s changed is the economics, and the rapid performance increase of LLMs.
Thanks to lower costs and better models, we are no longer just generating text. We’re generating outcomes.
That means we can get slides from a lecture video, organized notes from raw transcripts, booking flights, summarizing emails by urgency or importance; all using AI Agents.
In other words, LLMs are now becoming doers.
And that is why everyone is talking about Agentic AI.

